Posterior Interosseous Nerve Syndrome Vs Radial Tunnel Syndrome
Posterior interosseous nerve syndrome vs radial tunnel syndrome. The median nerve may become entrapped in the proximal forearm which can result in a variety of symptoms. Unlike carpal tunnel syndrome radial tunnel syndrome does not present tingling or numbness since the posterior interosseous nerve mainly affects motor function. In comparison the most common neuropathy carpal tunnel syndrome has an annual incidence between 01 and 035 in the general population 11 12.
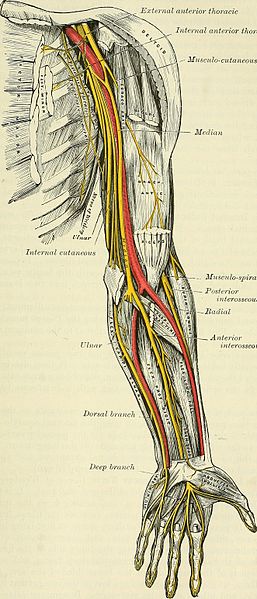
Conventional electromyographic and nerve-conduction studies usually do not show abnormalities in patients who have a clinical diagnosis of radial tunnel syndrome. Radial tunnel syndrome RTS and posterior interosseous nerve PIN compression syndrome are pathologic conditions that are believed to have the same etiology. It has no specific radiologic or electrodiagnostic findings.
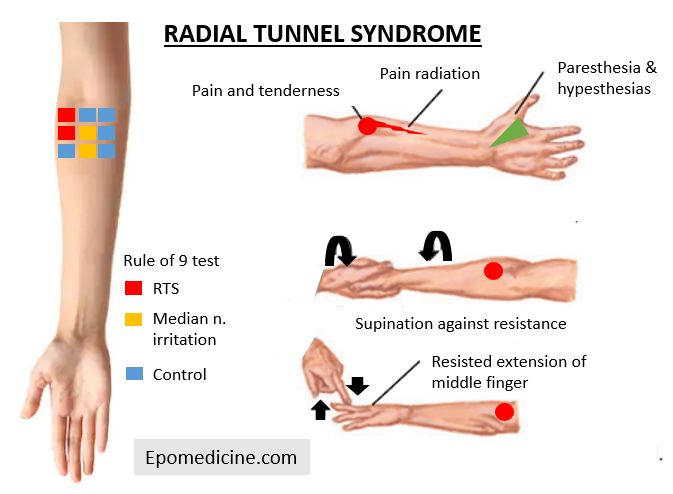
This problem is often caused by. Pain is not a distinct feature of posterior interosseous nerve entrapment. Diagnosis is made clinically with pain only maximal tenderness 3-5 cm distal to lateral epicondyle without any motor or.
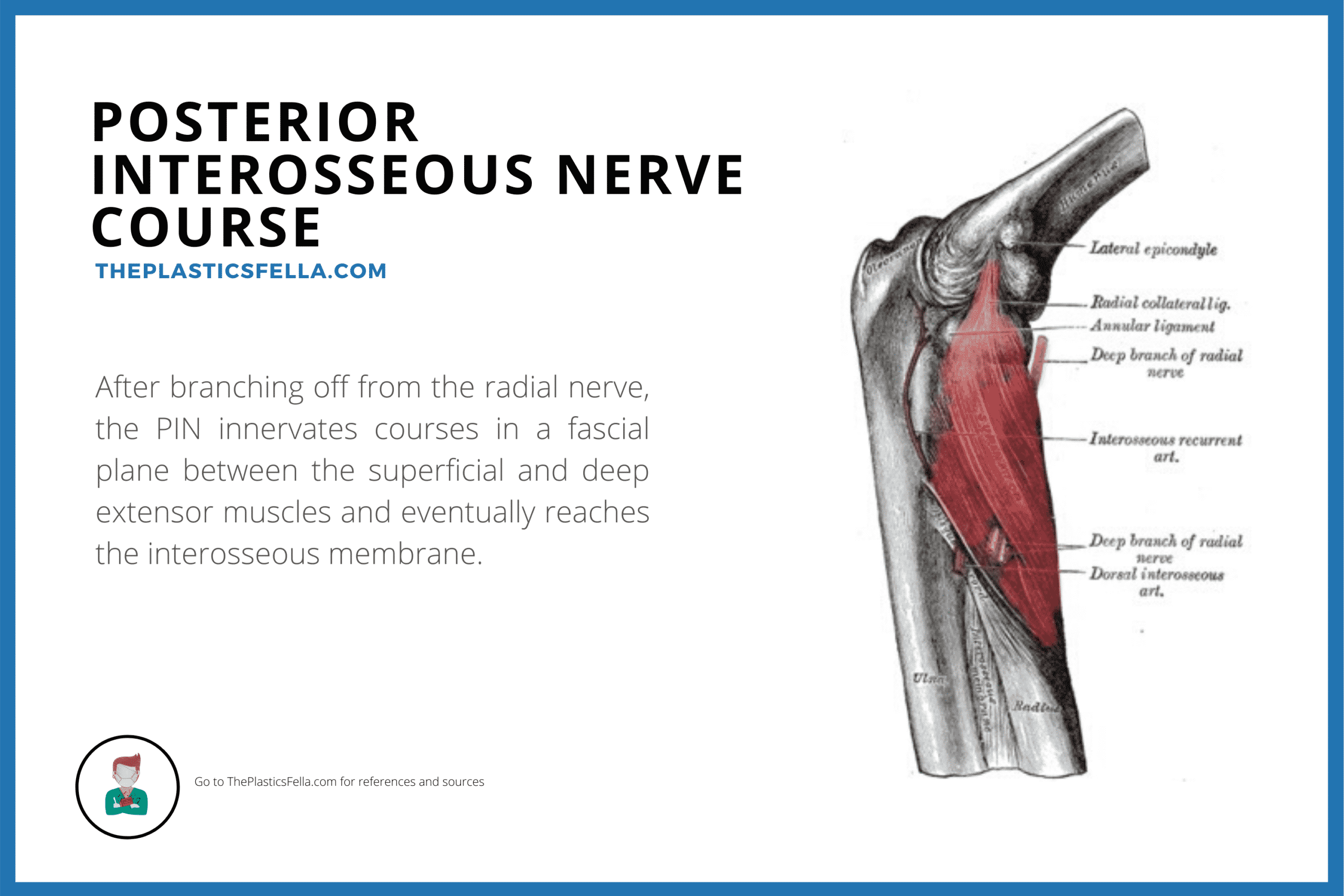
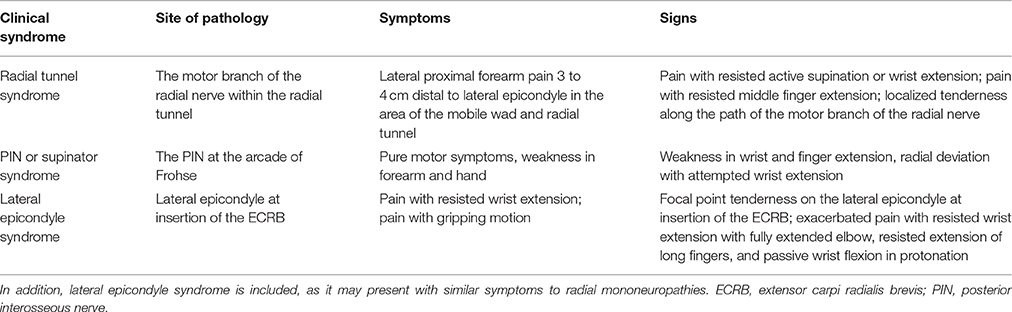
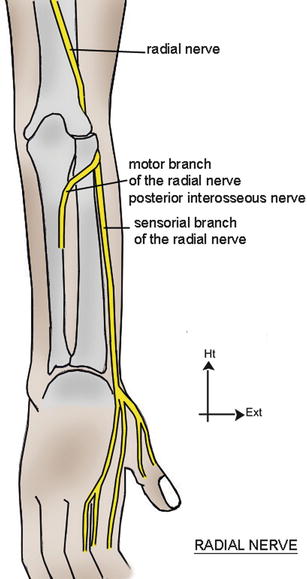
Radial nerve branch disorders at the elbow fall into two distinct clinical presentations. The posterior interosseous nerve is also stressed during passive supination elongation and rotation and during passive pronation compression. The annual incidence rate of the posterior interosseous nerve PIN compression is estimated 003 while the rate for superficial radial nerve SRN compression is 0003 10 11.
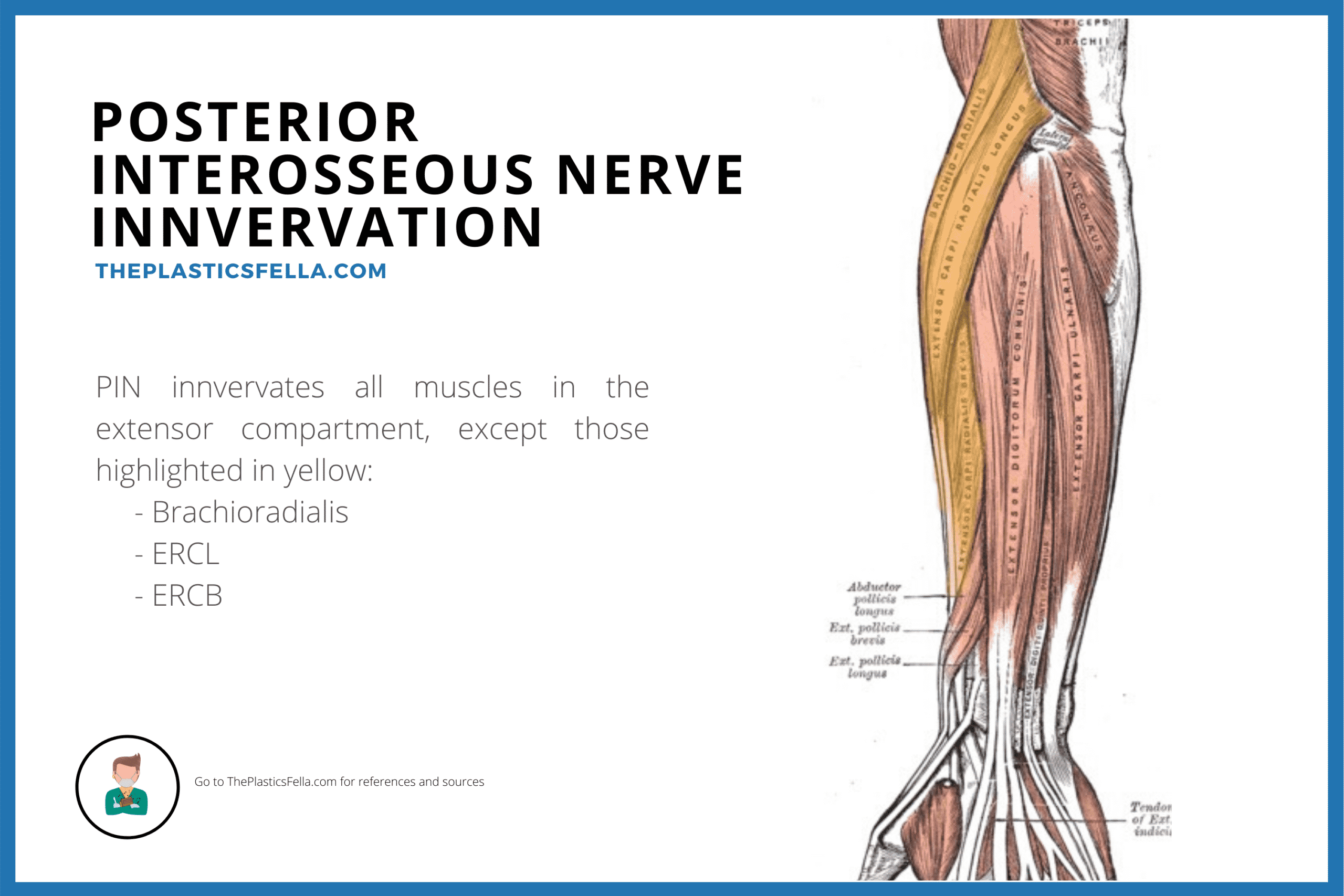
2 Compression of the superficial sensory branch Wartenbergs syndrome results in purely sensory symptoms while compression of the posterior interosseous nerve produces. Radial Tunnel Syndrome RTS and Posterior Interosseous Nerve Syndrome PINS. Patients with this palsy have loss of finger and thumb extension radial deviation on wrist extension ERCL is preserved.
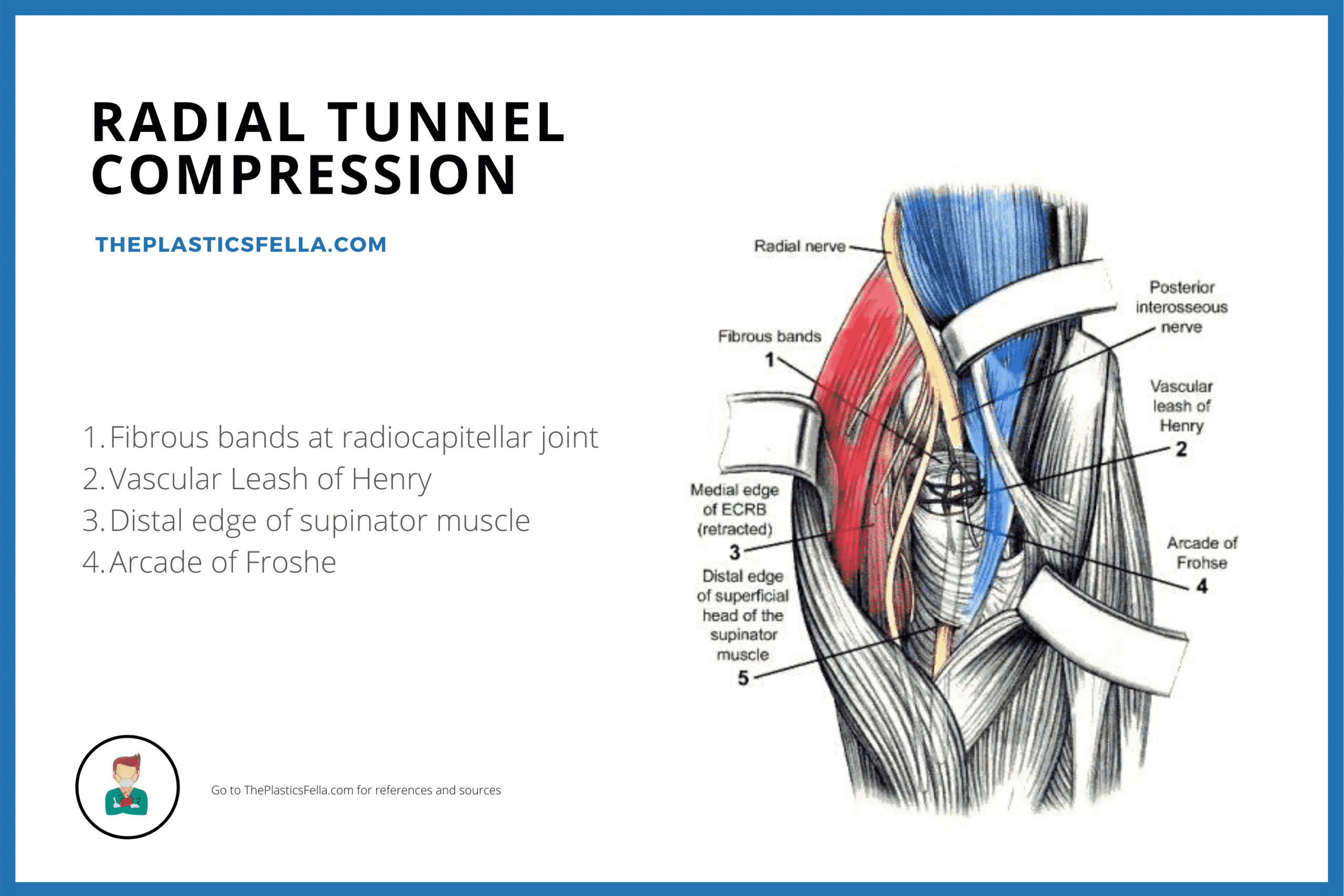
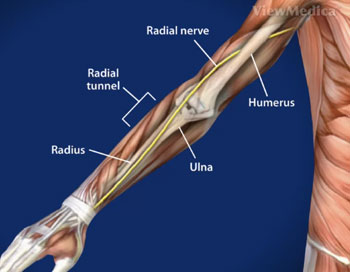
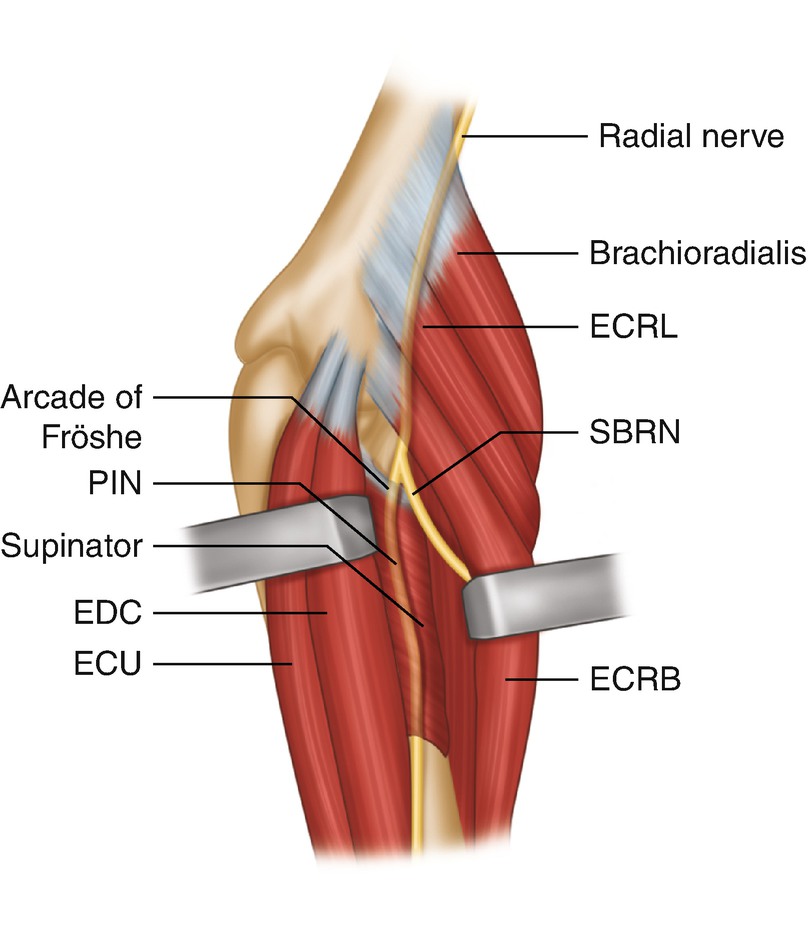
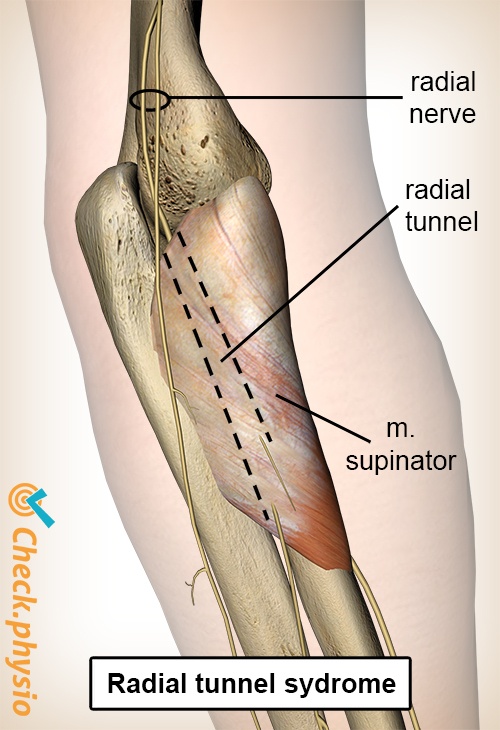
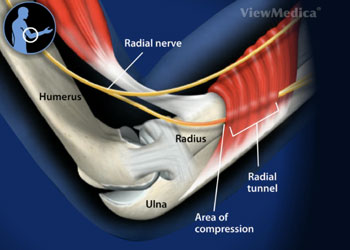
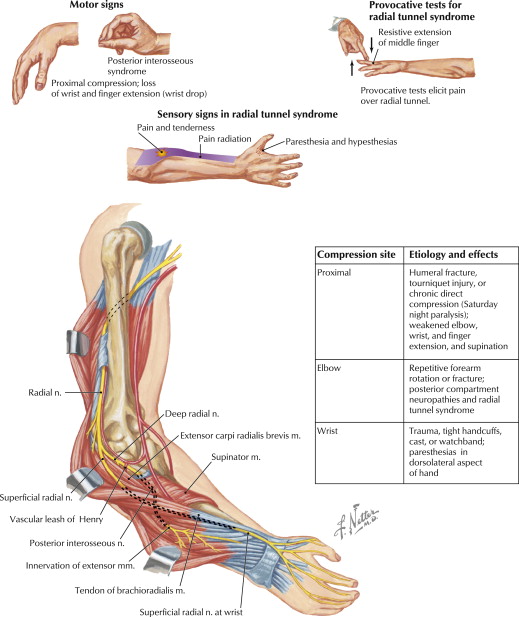
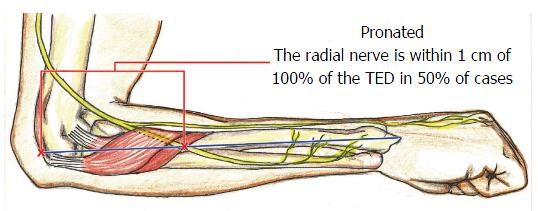
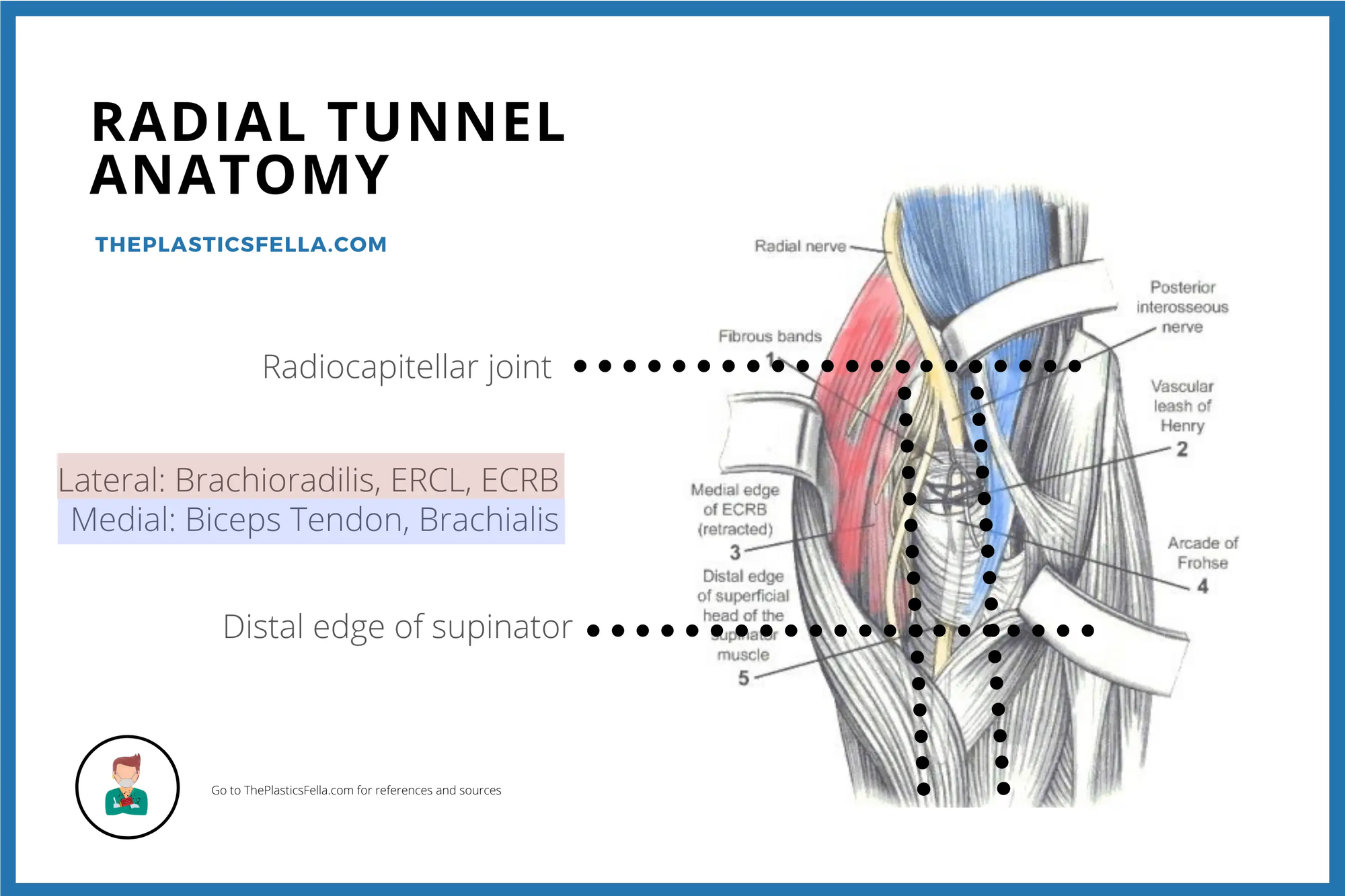
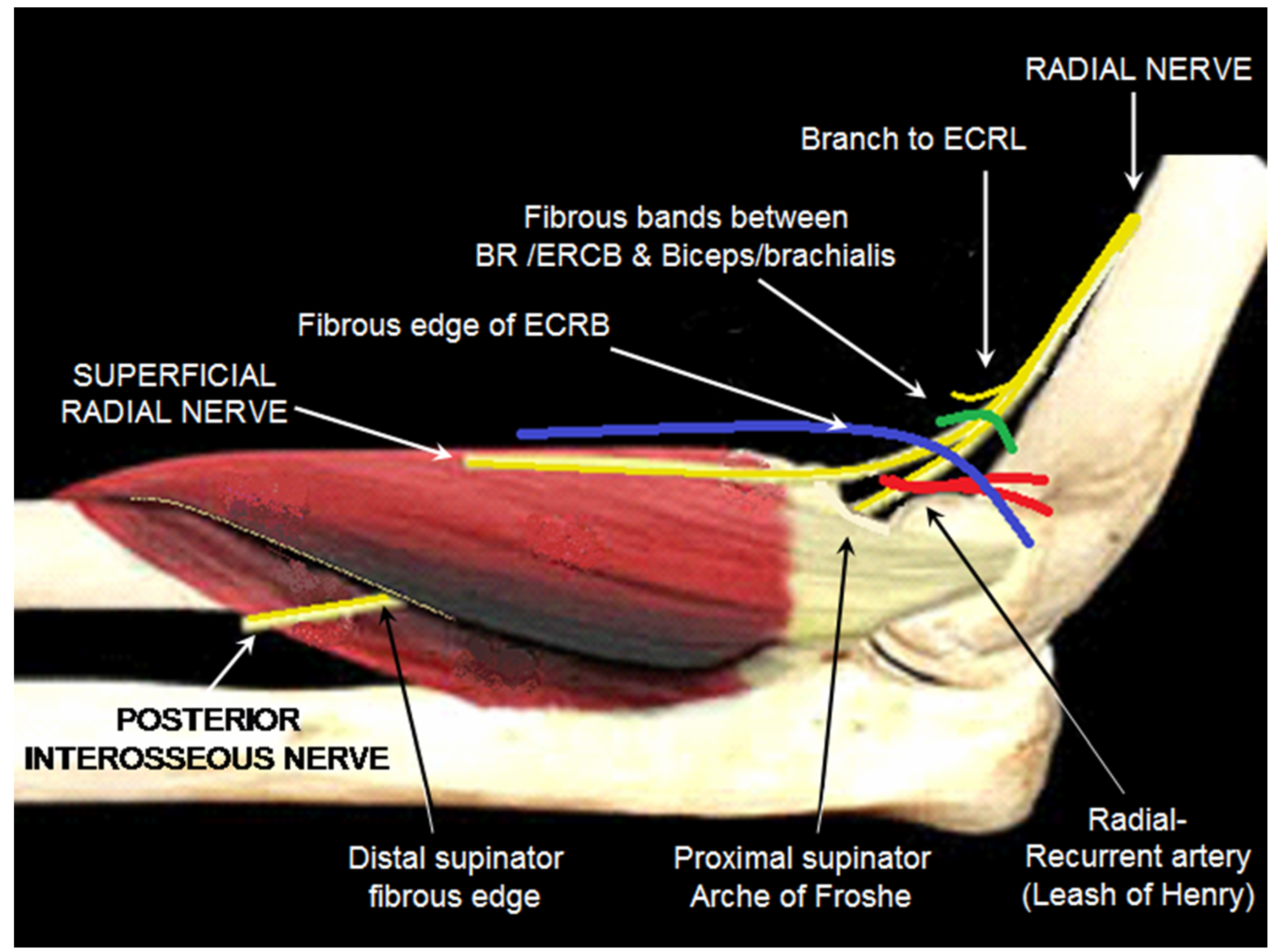
There are multiple potential sites of compression in the radial tunnel that may affect the sensory branch of the radial nerve the motor branch- also called the posterior interosseous nerve or both. Radial tunnel syndrome is a compressive neuropathy of the posterior interosseous nerve PIN at the level of proximal forearm radial tunnel. Posterior Interosseous Neuropathy.
In parts of the medical community Radial Tunnel Syndrome and PIN Syndrome are one in the same while in other parts they are different diagnoses with the same nerve involvement Posterior Interosseous Nerve. Pain and tenderness is less common than in radial tunnel syndrome.
The median nerve may become entrapped in the proximal forearm which can result in a variety of symptoms.
Τhe former is characterized by chronic elbow and forearm pain radiating to the wrist and dorsum of the hand and fingers whereas the latter should be considered when weakness or palsy of. In comparison the most common neuropathy carpal tunnel syndrome has an annual incidence between 01 and 035 in the general population 11 12. The absence of significant motor weakness differentiates this from Posterior Interosseous Nerve Syndrome Radial Tunnel Syndrome What is the objective for Radial Tunnel Syndrome. Radial tunnel syndrome is a pain syndrome resulting from compression of the posterior interosseous nerve at the proximal forearm. Conventional electromyographic and nerve-conduction studies usually do not show abnormalities in patients who have a clinical diagnosis of radial tunnel syndrome. Unlike carpal tunnel syndrome radial tunnel syndrome does not present tingling or numbness since the posterior interosseous nerve mainly affects motor function. Lesions of the RN or its motor branch can occur at any point along. This suggests that the interosseous nerve distal to the supinator muscle should be explored in radial tunnel compression syndromes. Radial tunnel syndrome RTS and posterior interosseous nerve PIN compression syndrome are pathologic conditions that are believed to have the same etiology.
In both cases the posterior interosseous nerve is entrapped or compressed within the radial tunnel Lutz 1991. Radial Tunnel Syndrome RTS and Posterior Interosseous Nerve Syndrome PINS. Pain and tenderness is less common than in radial tunnel syndrome. Posterior Interosseous Nerve PIN Syndrome is a pathology that involves pain andor motor weakness as a result of nerve compression. Radial nerve branch disorders at the elbow fall into two distinct clinical presentations. If not successful surgical treatment is indicated. Lesions of the RN or its motor branch can occur at any point along.














/radial-nerve-injury-2488802-FINAL-fd11d7465f8f465db5848ea726e89b65.png)















Post a Comment for "Posterior Interosseous Nerve Syndrome Vs Radial Tunnel Syndrome"