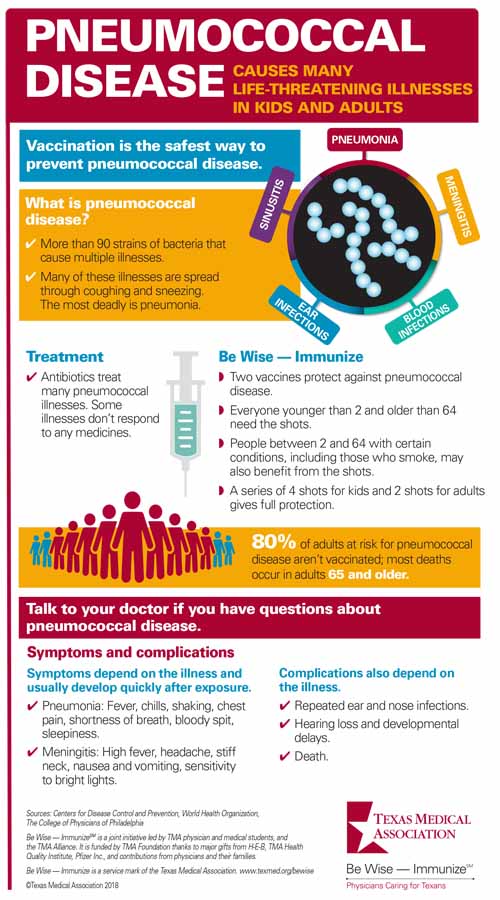
Pneumococcal Disease In Adults
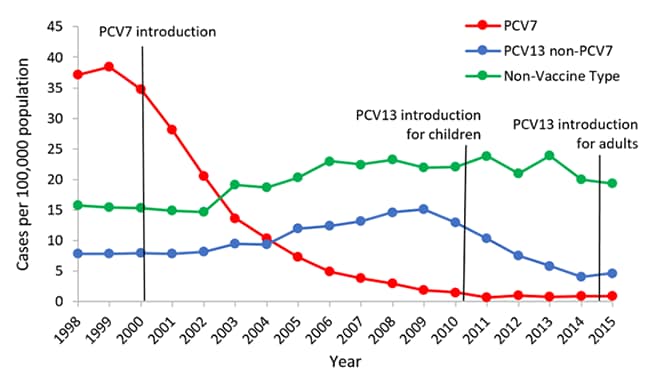
Pneumococcal disease in adults. Pneumococcal pneumonia causes an estimated 150000 hospitalizations each year in the United States. Up to half of hospitalised pneumonia in adults. Overall invasive pneumococcal disease in adults 19 through 64 years old decreased from 16 cases per 100000 people in 1998 to 8 cases per 100000 people in 2018.
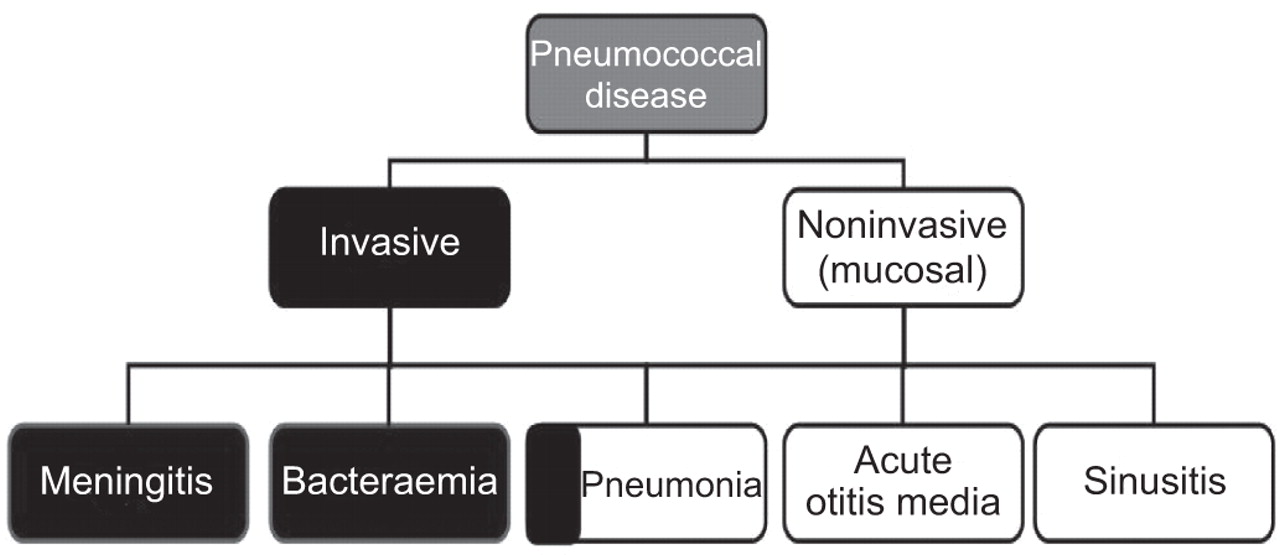
Pneumococcal disease can be very serious. Within the cluster of invasive pneumococcal diseases pneumonia also represents the most common infectious source. For PCV administration to infants WHO recommends three primary doses given at 6 10 and 14 weeks or 2 4 and 6 months or two primary doses plus a booster given between the age of 9 and 15 months.
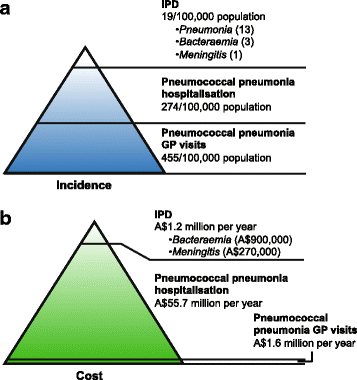
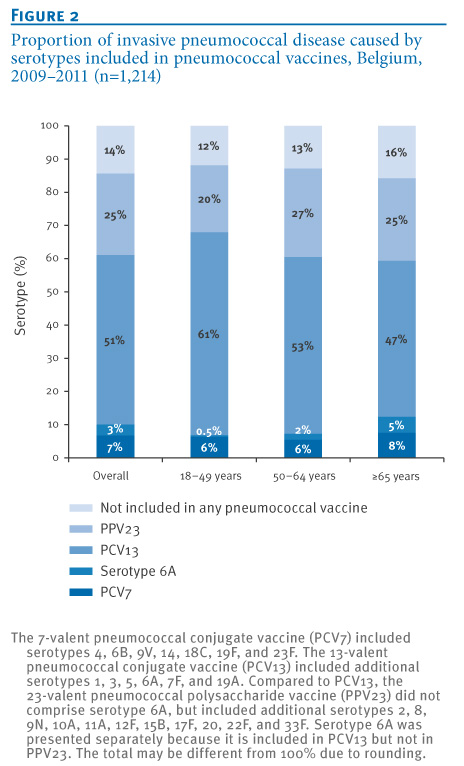
This population could also be targeted for an expanded valency conjugate vaccine. In these regions the annual incidence of invasive pneumococcal disease ranges from 10 to 100 cases per 100 000 population. What happens when someone gets pneumococcal disease.
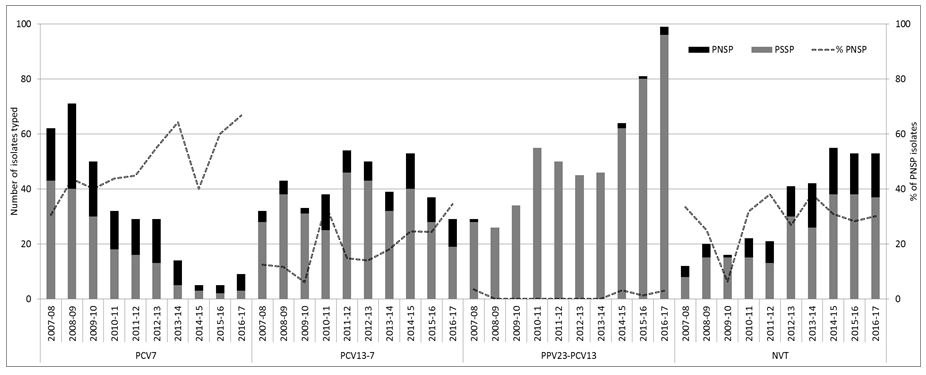
Invasive pneumococcal disease caused by the 13 serotypes included in PCV13 decreased in adults 19 through 64 years old from 11 cases per 100000 in 1998 to 2 cases per 100000 people in 2018. The overall likelihood of approval of a Phase I pneumococcal vaccine is 167 and the average probability a vaccine advances from Phase III is. Pneumoniae bacteria known as serotypes some of which cause more serious infection than others.
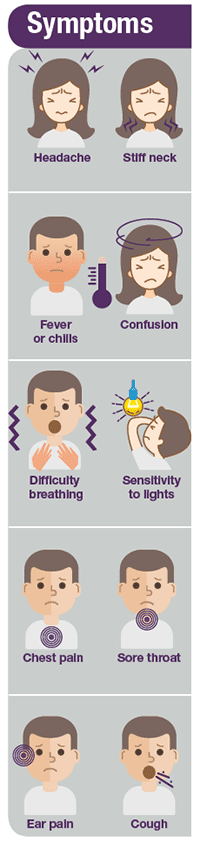
Pneumococcal disease in adults. Learn about pneumococcal disease symptoms and complications. Although it is widely accepted that adults with immunocompromising conditions are at greatly increased risk of pneumococcal infection the extent of risk among immunocompetent adults with chronic medical conditions is less certain particularly in the current era of universal vaccination of children with pneumococcal conjugate vaccines.
The burden of non-invasive pneumococcal disease in adults is mainly determined by community-acquired pneumonia. Pneumoniae is the most common cause of community-acquired bacterial pneumonia in adults. Although it is widely accepted that adults with immunocompromising conditions are at greatly increased risk of pneumococcal infection the extent of risk among immunocompetent adults with chronic medical conditions is less certain particularly in the current era of universal vaccination of children with pneumococcal conjugate vaccines.
297 40 were at greater risk of PP and IPD compared with their healthy counterparts. The incidence of IPD in adults with certain haematological and solid-organ malignancies is significantly greater than the overall adult population.
What happens when someone gets pneumococcal disease.
The burden of non-invasive pneumococcal disease in adults is mainly determined by community-acquired pneumonia. The risks of invasive pneumococcal disease in persons with specific chronic illnesses was compared with that in healthy adults controlling for age race and the other chronic illnesses. Although it is widely accepted that adults with immunocompromising conditions are at greatly increased risk of pneumococcal infection the extent of risk among immunocompetent adults with chronic medical conditions is less certain particularly in the current era of universal vaccination of children with pneumococcal conjugate vaccines. In addition PCV13 is licensed for the prevention of pneumococcal disease in adults 50 years of age. The incidence of IPD in adults with certain haematological and solid-organ malignancies is significantly greater than the overall adult population. Pneumococcal meningitis and bacteremia killed approximately 3500 people in the United States in 2018. Within the cluster of invasive pneumococcal diseases pneumonia also represents the most common infectious source. Learn about pneumococcal disease symptoms and complications. About pneumococcal infections Pneumococcal infections are caused by the Streptococcus pneumoniae bacteria and range from mild to severe.
297 40 were at greater risk of PP and IPD compared with their healthy counterparts. 126 to 433 44 to 71 adults with two or more medical conditions PP. Pneumoniae bacteria known as serotypes some of which cause more serious infection than others. 187 58 and high-risk adults PP. Pneumococcal pneumonia has high incidence rates and carries a high mortality risk especially in the elderly. More than one-third of all community-acquired pneumonia. Invasive pneumococcal disease caused by the 13 serotypes included in PCV13 decreased in adults 19 through 64 years old from 11 cases per 100000 in 1998 to 2 cases per 100000 people in 2018.








































Post a Comment for "Pneumococcal Disease In Adults"