Pneumonia In Cattle Treatment
Pneumonia in cattle treatment. The most important step in any calf health-management programme is a successful colostrum-management programme. Treatment focuses on antimicrobial therapy to control secondary bacterial pneumonia see Bacterial Pneumonia in Cattle. Every herd of cattle whether or not pneumonia is a problem.
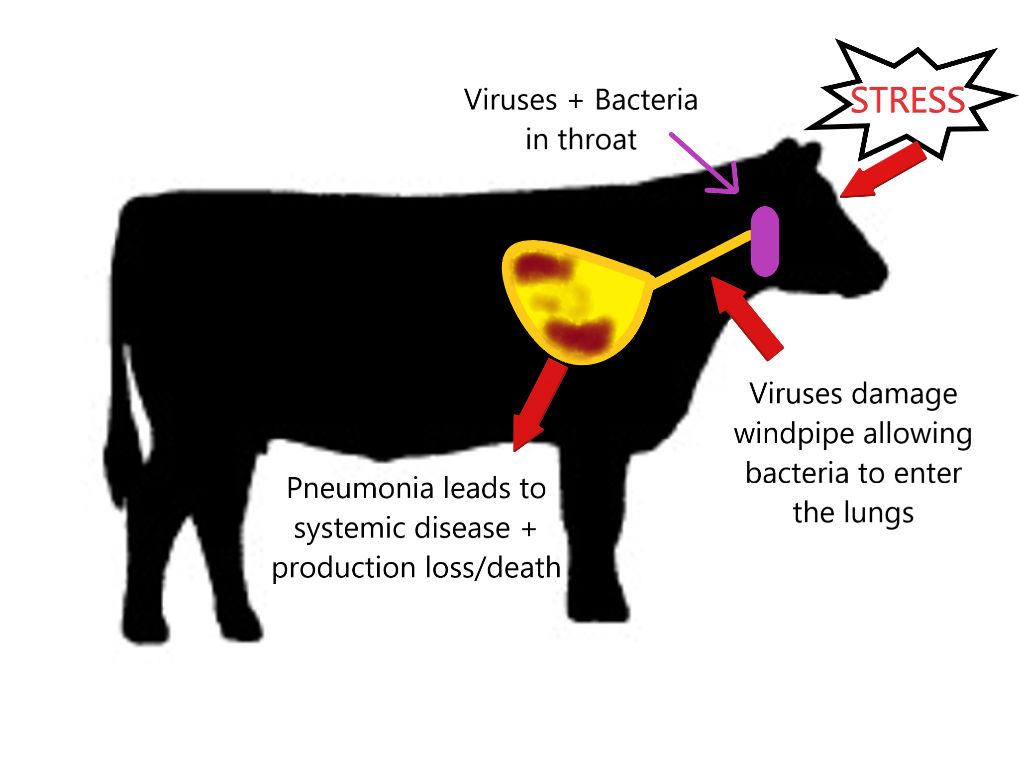
However improvement is usually marked when cattle are turned out in the spring. In dogs and less frequently in cats aspiration pneumonia is generally associated with inhalation of oral ingesta regurgitated material or vomitus. Strategies to reduce pneumonia should target improving cattle immunity and reducing stress as well as treating any disease present.
However for bacterial pneumonia in cattle sheep and pigs penicillin G is not. Bovine respiratory syncytial virus BRSV is the most common virus found in pneumonia cases in calves. Cattle with extremely low blood concentrations of the trace elements selenium and copper have.
On occasion a farm may experience an outbreak of IBR but use of intranasal vaccines has reduced the frequency of finding this virus in calves. The publication presents a review of potential causes and discusses the environmental links to the clinical observations of the condition. The following steps should reduce the risk of pneumonia in feeder calves.
Supportive therapy and correction of dehydration may be necessary. Calves that are not given enough antibodies at birth are at increased risk for pneumonia and scours throughout the entire growing period. Vitamins can be administered as a supportive therapy and a multitude of treatments from antihistamines to expectorants have been found effective in alleviating the condition.
Because it is often impossible to completely shield cattle from further challenge most recover only partially after dexamethasone treatment 1 mg510 kg body wt. Studies have shown that when 30 per cent of cattle in a group show actual signs of respiratory disease a further 40 per cent can exhibit lung damage at slaughter. While early antibiotic treatment can be very effective in reducing the losses caused by the disease.
This video is for animal husbandry and animal friend only. Respiratory changes differ depending on the type and stage of pneumonia and could include changes in the rate and depth of respiration nasal discharge and coughing.
The factors that allow the micro-organisms to cause the disease are those that are under the control of the management or are a result of the husbandry system.
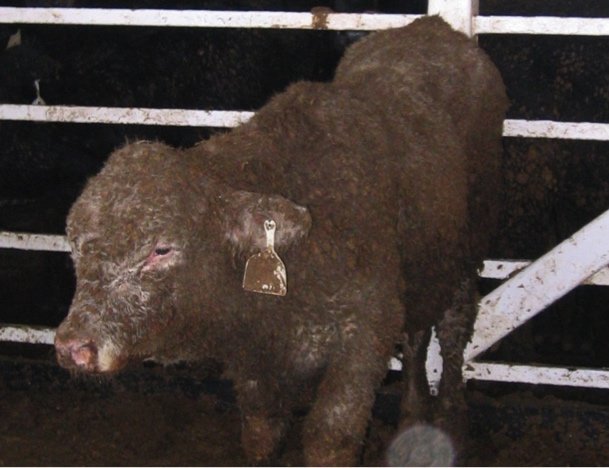
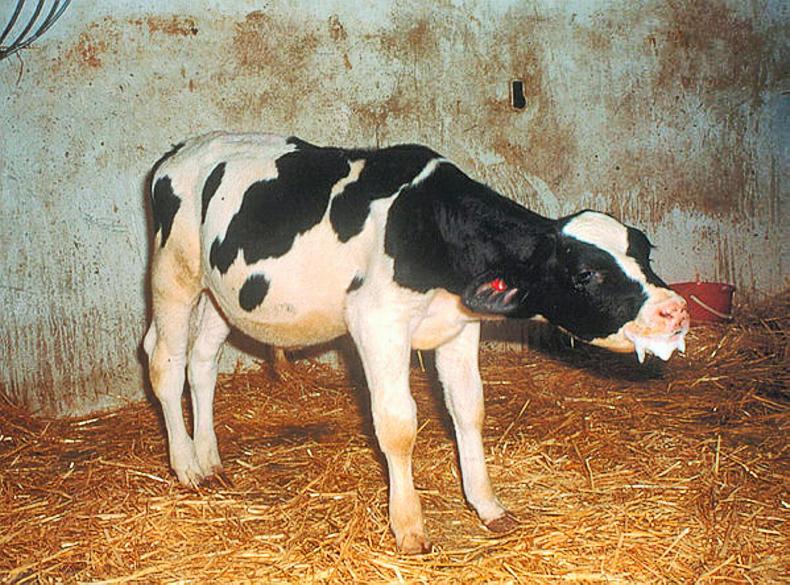
Supportive therapy and correction of dehydration may be necessary. Studies have shown that when 30 per cent of cattle in a group show actual signs of respiratory disease a further 40 per cent can exhibit lung damage at slaughter. The general rule of thumb is to treat animals with temperatures above 104 F 40 C. Pneumonia may easily be treated and prevented by isolating sick calves using proper management techniques vaccinating young calves providing good ventilation and using antibiotics as necessary. However improvement is usually marked when cattle are turned out in the spring. Respiratory changes differ depending on the type and stage of pneumonia and could include changes in the rate and depth of respiration nasal discharge and coughing. Strategies to reduce pneumonia should target improving cattle immunity and reducing stress as well as treating any disease present. There is no specific treatment for the viral interstitial pneumonia. Calves that are not given enough antibodies at birth are at increased risk for pneumonia and scours throughout the entire growing period.
Calves that are not given enough antibodies at birth are at increased risk for pneumonia and scours throughout the entire growing period. Use of an intranasal vaccine for. Treatment focuses on antimicrobial therapy to control secondary bacterial pneumonia see Bacterial Pneumonia in Cattle. The publication presents a review of potential causes and discusses the environmental links to the clinical observations of the condition. All material provided by this channel is for educational purposes onlyYou Should Use Any Medicine. The factors that allow the micro-organisms to cause the disease are those that are under the control of the management or are a result of the husbandry system. Every herd of cattle whether or not pneumonia is a problem.



































Post a Comment for "Pneumonia In Cattle Treatment"